When DNA Repair Goes Wrong
Within the genome there exist short, repeating segments of DNA - motifs of, typically, one through six base pairs that repeat five to 50 times1. These segments of DNA are known as microsatellites and comprise approximately 3% of the human genome, in both coding and noncoding regions of the genome2,3. Microsatellites are particularly susceptible to accumulating mutations during DNA replication. This phenomenon is known as microsatellite instability, or MSI. Microsatellites have a mutation rate of 10-100-fold higher than the average DNA segment4. These mutations are hypothesized to be caused by slipped strand mispairing5, where the DNA polymerase disengages from the DNA and reassociates at a nearby but different location.
Because microsatellites are disproportionately mutated, they can be utilized as markers of DNA damage that causes cancer and other diseases. When every process in the cell is working properly, mutations in microsatellites can be repaired by the canonical mismatch repair processes. However, the genes involved in the mismatch repair process including MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 are frequently mutated, and the resulting DNA damage that is not repaired can cause disease. MSH2 and MSH6 dimerize to form the heterodimer MutS alpha6, which initiates the mismatch repair pathway by binding to small, single and dinucleotide errors in the DNA. Another heterodimer, MutL alpha, is formed by MLH1 and PMS2, and recruits exonucleases or DNA polymerase III to the site of the mismatch7. These are just a few of the many proteins involved in the mismatch repair process, but are the most frequently mutated themselves.
Lynch syndrome is one disease caused by mutations in genes that code for proteins in the mismatch repair pathway. Also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer, Lynch syndrome is a heritable disease caused by mutations in MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 as well as EPCAM8 and leads to a variety of cancers including - primarily - colorectal cancer, as well as ovarian, stomach, endometrial, urinary tract, bowel, brain, pancreatic, prostate, and biliary tract cancers8,9. Endometrial cancer is the second most common cancer to be caused in Lynch syndrome, and is more common than colon cancer amongst women with the disease10.
Even in non-heritable cancers, microsatellite instability is a marker of poor prognosis. One study looked in 18 different types of cancer and observed that microsatellite instability was present in specimens from 14, including endometrial cancer, renal cancer, colon cancer, and stomach cancer, all of which can be subtyped clinically by the presence of microsatellite instability11.
Several neurologic disorders, including Huntington’s disease, are caused by a microsatellite repeat. However, the mismatch repair pathway is actually deleterious in this disease; recent studies in a mouse model showed that lack of MSH2 delays the onset of disease symptoms by preventing the lengthening of the microsatellite region that would otherwise occur during the repair process12.
Bethyl's extensive DNA Repair portfolio contains hundreds of antibodies, including MSH2, MSH6, and EpCAM.
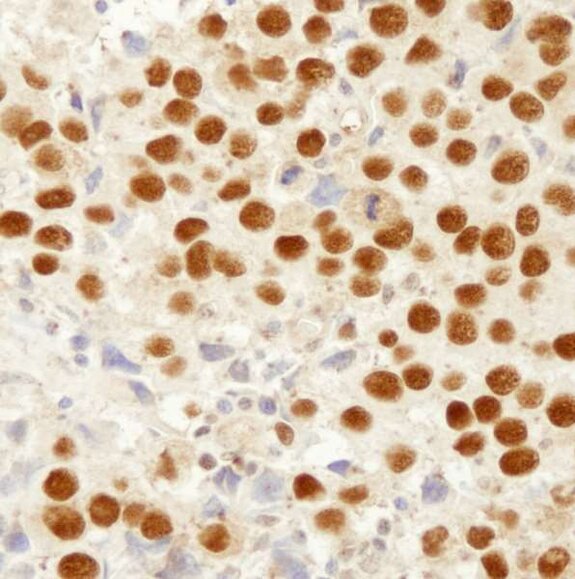
Detection of human MSH2 by immunohistochemistry. Sample: FFPE section of human seminoma. Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-MSH2 (Cat. No. IHC-00082) used at a dilution of 1:250. Detection: DAB.
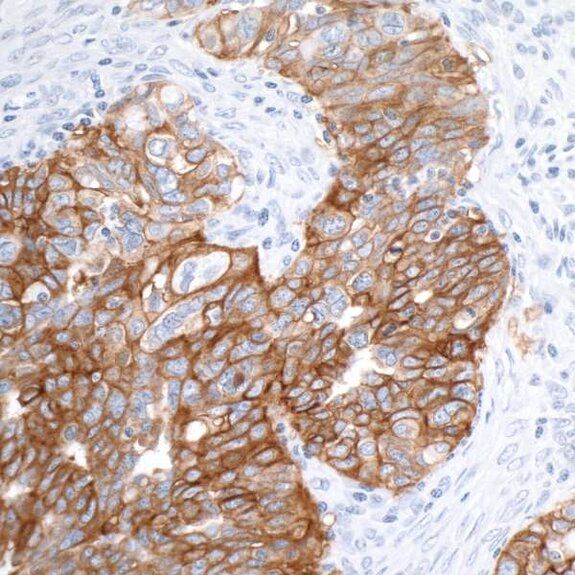
Detection of human EpCAM in FFPE ovarian carcinoma by IHC. Antibody: Rabbit anti-EpCAM recombinant monoclonal [BLR077G] (A700-077). Secondary: HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (A120-501P). Substrate: DAB.
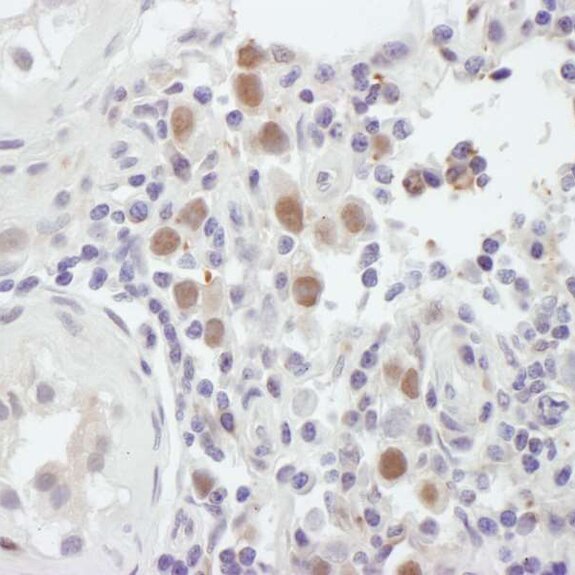
Detection of human MSH6 by immunohistochemistry. Sample: FFPE section of human testicular seminoma. Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-MSH6 (Cat. No. A300-023A Lot2) used at a dilution of 1:500 (2µg/ml). Detection: DAB.
References
- Gologan A, Sepulveda AR (2005) Microsatellite Instability and DNA Mismatch Repair Deficiency Testing in Hereditary and Sporadic Gastrointestinal Cancers. Clinics in Laboratory Medicine 25:179–196.
- Subramanian S, Mishra RK, Singh L (2003). Genome-wide analysis of microsatellite repeats in humans: their abundance and density in specific genomic regions. Genome Biology 4:R13.
- Toth G (2000) Microsatellites in Different Eukaryotic Genomes: Survey and Analysis. Genome Research 10:967–981.
- Eckert KA, Hile SE (2009) Every microsatellite is different: Intrinsic DNA features dictate mutagenesis of common microsatellites present in the human genome. Molecular Carcinogenesis 48:379–388.
- Levinson G, Gutman GA (1987) Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Molecular Biology and Evolution.
- Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. (2020) MSH6 Muts Homolog 6 [Homo Sapiens (Human)] – Gene – NCBI. [online] Available at: NCBI Gene record for MSH6 [Accessed 14 May 2020]
- Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. (2020) MLH1 mutL homolog 1 (Homo sapiens, human) – Gene – NCBI. [online] Accessed 14 May 2020.
- Rahner N, Steinke V, Schlegelberger B, Olschwang S, Eisinger F, Hutter P (2010) Clinical utility gene card for: Lynch syndrome (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2). European Journal of Human Genetics 18:1071–1071.
- Cox VL, Saeed Bamashmos AA, Foo WC, Gupta S, Yedururi S, Garg N, Kang HC (2018) Lynch Syndrome: Genomics Update and Imaging Review. RadioGraphics 38:483–499.
- Aarnio M, Sankila R, Pukkala E, Salovaara R, Aaltonen LA, de la Chapelle A, Peltomäki P, Mecklin J-P, Järvinen HJ (1999) Cancer risk in mutation carriers of DNA-mismatch-repair genes. International Journal of Cancer 81:214–218 . <214::aid-ijc8>3.0.co;2-l
- Hause RJ, Pritchard CC, Shendure J, Salipante SJ (2016) Classification and characterization of microsatellite instability across 18 cancer types. Nature Medicine 22:1342–1350.
- Wheeler VC (2003) Mismatch repair gene Msh2 modifies the timing of early disease in HdhQ111 striatum. Human Molecular Genetics 12:273–281.